This section describes the time zone settings maintained by MySQL, how to load the system tables required for named time support, how to stay current with time zone changes, and how to enable leap-second support.
- Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Portal
- Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Download
- Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Mac
- Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Ubuntu
DBeaver Universal Database Tool Free multi-platform database tool for developers, database administrators, analysts and all people who need to work with databases. Supports all popular databases: MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLite, Oracle, DB2, SQL Server, Sybase, MS Access, Teradata, Firebird, Apache Hive, Phoenix, Presto, etc. DBeaver is a database management tool with a graphical interface similar to SQL Server Management Studio (SSMS). However, SSMS is only available on Windows machines, so if you run Mac or Linux, you need to look for alternatives. Fortunately, DBeaver steps up as a popular (and free) alternative.
For information about time zone settings in replication setups, see Section 16.4.1.15, 'Replication and System Functions' and Section 16.4.1.31, 'Replication and Time Zones'.
MySQL Server maintains several time zone settings:
The system time zone. When the server starts, it attempts to determine the time zone of the host machine automatically and uses it to set the
system_time_zonesystem variable. The value does not change thereafter.To explicitly specify the system time zone for MySQL Server at startup, set the
TZenvironment variable before you start mysqld. If you start the server using mysqld_safe, its--timezoneoption provides another way to set the system time zone. The permissible values forTZand--timezoneare system dependent. Consult your operating system documentation to see what values are acceptable.The server current time zone. The global
time_zonesystem variable indicates the time zone the server currently is operating in. The initialtime_zonevalue is'SYSTEM', which indicates that the server time zone is the same as the system time zone.If set to
SYSTEM, every MySQL function call that requires a time zone calculation makes a system library call to determine the current system time zone. This call may be protected by a global mutex, resulting in contention.The initial global server time zone value can be specified explicitly at startup with the
--default-time-zoneoption on the command line, or you can use the following line in an option file:If you have the
SUPERprivilege, you can set the global server time zone value at runtime with this statement:Per-session time zones. Each client that connects has its own session time zone setting, given by the session
time_zonevariable. Initially, the session variable takes its value from the globaltime_zonevariable, but the client can change its own time zone with this statement:
The session time zone setting affects display and storage of time values that are zone-sensitive. This includes the values displayed by functions such as NOW() or CURTIME(), and values stored in and retrieved from TIMESTAMP columns. Values for TIMESTAMP columns are converted from the session time zone to UTC for storage, and from UTC to the session time zone for retrieval.
The session time zone setting does not affect values displayed by functions such as UTC_TIMESTAMP() or values in DATE, TIME, or DATETIME columns. Nor are values in those data types stored in UTC; the time zone applies for them only when converting from TIMESTAMP values. If you want locale-specific arithmetic for DATE, TIME, or DATETIME values, convert them to UTC, perform the arithmetic, and then convert back.
The current global and session time zone values can be retrieved like this:
timezone values can be given in several formats, none of which are case-sensitive:
As the value
'SYSTEM', indicating that the server time zone is the same as the system time zone.As a string indicating an offset from UTC of the form
[, prefixed with aH]H:MM+or-, such as'+10:00','-6:00', or'+05:30'. A leading zero can optionally be used for hours values less than 10; MySQL prepends a leading zero when storing and retriving the value in such cases. MySQL converts'-00:00'or'-0:00'to'+00:00'.A time zone offset must be in the range
'-12:59'to'+13:00', inclusive.As a named time zone, such as
'Europe/Helsinki','US/Eastern','MET', or'UTC'.Named time zones can be used only if the time zone information tables in the
mysqldatabase have been created and populated. Otherwise, use of a named time zone results in an error:
Several tables in the mysql system database exist to store time zone information (see Section 5.3, 'The mysql System Database'). The MySQL installation procedure creates the time zone tables, but does not load them. To do so manually, use the following instructions.
Loading the time zone information is not necessarily a one-time operation because the information changes occasionally. When such changes occur, applications that use the old rules become out of date and you may find it necessary to reload the time zone tables to keep the information used by your MySQL server current. See Staying Current with Time Zone Changes.
If your system has its own zoneinfo database (the set of files describing time zones), use the mysql_tzinfo_to_sql program to load the time zone tables. Examples of such systems are Linux, macOS, FreeBSD, and Solaris. One likely location for these files is the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory. If your system has no zoneinfo database, you can use a downloadable package, as described later in this section.
The system time zone. When the server starts, it attempts to determine the time zone of the host machine automatically and uses it to set the
system_time_zonesystem variable. The value does not change thereafter.To explicitly specify the system time zone for MySQL Server at startup, set the
TZenvironment variable before you start mysqld. If you start the server using mysqld_safe, its--timezoneoption provides another way to set the system time zone. The permissible values forTZand--timezoneare system dependent. Consult your operating system documentation to see what values are acceptable.The server current time zone. The global
time_zonesystem variable indicates the time zone the server currently is operating in. The initialtime_zonevalue is'SYSTEM', which indicates that the server time zone is the same as the system time zone.If set to
SYSTEM, every MySQL function call that requires a time zone calculation makes a system library call to determine the current system time zone. This call may be protected by a global mutex, resulting in contention.The initial global server time zone value can be specified explicitly at startup with the
--default-time-zoneoption on the command line, or you can use the following line in an option file:If you have the
SUPERprivilege, you can set the global server time zone value at runtime with this statement:Per-session time zones. Each client that connects has its own session time zone setting, given by the session
time_zonevariable. Initially, the session variable takes its value from the globaltime_zonevariable, but the client can change its own time zone with this statement:
The session time zone setting affects display and storage of time values that are zone-sensitive. This includes the values displayed by functions such as NOW() or CURTIME(), and values stored in and retrieved from TIMESTAMP columns. Values for TIMESTAMP columns are converted from the session time zone to UTC for storage, and from UTC to the session time zone for retrieval.
The session time zone setting does not affect values displayed by functions such as UTC_TIMESTAMP() or values in DATE, TIME, or DATETIME columns. Nor are values in those data types stored in UTC; the time zone applies for them only when converting from TIMESTAMP values. If you want locale-specific arithmetic for DATE, TIME, or DATETIME values, convert them to UTC, perform the arithmetic, and then convert back.
The current global and session time zone values can be retrieved like this:
timezone values can be given in several formats, none of which are case-sensitive:
As the value
'SYSTEM', indicating that the server time zone is the same as the system time zone.As a string indicating an offset from UTC of the form
[, prefixed with aH]H:MM+or-, such as'+10:00','-6:00', or'+05:30'. A leading zero can optionally be used for hours values less than 10; MySQL prepends a leading zero when storing and retriving the value in such cases. MySQL converts'-00:00'or'-0:00'to'+00:00'.A time zone offset must be in the range
'-12:59'to'+13:00', inclusive.As a named time zone, such as
'Europe/Helsinki','US/Eastern','MET', or'UTC'.Named time zones can be used only if the time zone information tables in the
mysqldatabase have been created and populated. Otherwise, use of a named time zone results in an error:
Several tables in the mysql system database exist to store time zone information (see Section 5.3, 'The mysql System Database'). The MySQL installation procedure creates the time zone tables, but does not load them. To do so manually, use the following instructions.
Loading the time zone information is not necessarily a one-time operation because the information changes occasionally. When such changes occur, applications that use the old rules become out of date and you may find it necessary to reload the time zone tables to keep the information used by your MySQL server current. See Staying Current with Time Zone Changes.
If your system has its own zoneinfo database (the set of files describing time zones), use the mysql_tzinfo_to_sql program to load the time zone tables. Examples of such systems are Linux, macOS, FreeBSD, and Solaris. One likely location for these files is the /usr/share/zoneinfo directory. If your system has no zoneinfo database, you can use a downloadable package, as described later in this section.
To load the time zone tables from the command line, pass the zoneinfo directory path name to mysql_tzinfo_to_sql and send the output into the mysql program. For example:
The mysql command shown here assumes that you connect to the server using an account such as root that has privileges for modifying tables in the mysql system database. Adjust the connection parameters as required.
mysql_tzinfo_to_sql reads your system's time zone files and generates SQL statements from them. mysql processes those statements to load the time zone tables.
mysql_tzinfo_to_sql also can be used to load a single time zone file or generate leap second information:
To load a single time zone file
tz_filethat corresponds to a time zone nametz_name, invoke mysql_tzinfo_to_sql like this:With this approach, you must execute a separate command to load the time zone file for each named zone that the server needs to know about.
If your time zone must account for leap seconds, initialize leap second information like this, where
tz_fileis the name of your time zone file:
After running mysql_tzinfo_to_sql, restart the server so that it does not continue to use any previously cached time zone data.
Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Portal
If your system has no zoneinfo database (for example, Windows), you can use a package containing SQL statements that is available for download at the MySQL Developer Zone:
Do not use a downloadable time zone package if your system has a zoneinfo database. Use the mysql_tzinfo_to_sql utility instead. Otherwise, you may cause a difference in datetime handling between MySQL and other applications on your system.
To use an SQL-statement time zone package that you have downloaded, unpack it, then load the unpacked file contents into the time zone tables:
Then restart the server.
Do not use a downloadable time zone package that contains MyISAM tables. That is intended for older MySQL versions. MySQL 5.7 and higher uses InnoDB for the time zone tables. Trying to replace them with MyISAM tables causes problems.
When time zone rules change, applications that use the old rules become out of date. To stay current, it is necessary to make sure that your system uses current time zone information is used. For MySQL, there are multiple factors to consider in staying current:
Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Download
The operating system time affects the value that the MySQL server uses for times if its time zone is set to
SYSTEM. Make sure that your operating system is using the latest time zone information. For most operating systems, the latest update or service pack prepares your system for the time changes. Check the website for your operating system vendor for an update that addresses the time changes.If you replace the system's
/etc/localtimetime zone file with a version that uses rules differing from those in effect at mysqld startup, restart mysqld so that it uses the updated rules. Otherwise, mysqld might not notice when the system changes its time.If you use named time zones with MySQL, make sure that the time zone tables in the
mysqldatabase are up to date:If your system has its own zoneinfo database, reload the MySQL time zone tables whenever the zoneinfo database is updated.
For systems that do not have their own zoneinfo database, check the MySQL Developer Zone for updates. When a new update is available, download it and use it to replace the content of your current time zone tables.
For instructions for both methods, see Populating the Time Zone Tables. mysqld caches time zone information that it looks up, so after updating the time zone tables, restart mysqld to make sure that it does not continue to serve outdated time zone data.
If you are uncertain whether named time zones are available, for use either as the server's time zone setting or by clients that set their own time zone, check whether your time zone tables are empty. The following query determines whether the table that contains time zone names has any rows:
A count of zero indicates that the table is empty. In this case, no applications currently are using named time zones, and you need not update the tables (unless you want to enable named time zone support). A count greater than zero indicates that the table is not empty and that its contents are available to be used for named time zone support. In this case, be sure to reload your time zone tables so that applications that use named time zones obtain correct query results.
To check whether your MySQL installation is updated properly for a change in Daylight Saving Time rules, use a test like the one following. The example uses values that are appropriate for the 2007 DST 1-hour change that occurs in the United States on March 11 at 2 a.m.
The test uses this query:
The two time values indicate the times at which the DST change occurs, and the use of named time zones requires that the time zone tables be used. The desired result is that both queries return the same result (the input time, converted to the equivalent value in the 'US/Central' time zone).
Before updating the time zone tables, you see an incorrect result like this:
After updating the tables, you should see the correct result:
Leap second values are returned with a time part that ends with :59:59. This means that a function such as NOW() can return the same value for two or three consecutive seconds during the leap second. It remains true that literal temporal values having a time part that ends with :59:60 or :59:61 are considered invalid.
If it is necessary to search for TIMESTAMP values one second before the leap second, anomalous results may be obtained if you use a comparison with ' values. The following example demonstrates this. It changes the session time zone to UTC so there is no difference between internal YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss'TIMESTAMP values (which are in UTC) and displayed values (which have time zone correction applied).
To work around this, you can use a comparison based on the UTC value actually stored in the column, which has the leap second correction applied:
Step-by-step tutorial on connecting to SQL Server with DBeaver.
Once you've installed DBeaver, you'll probably want to connect to a database. below are instructions for connecting to SQL Server using DBeaver on a Mac.
Note that, although this tutorial uses SQL Server, DBeaver supports many different database management systems.
Launch DBeaver
Click on the DBeaver icon (either in your Launchpad or the Applications folder) to launch the DBeaver application.
Launch the New Connection Wizard
If this is the first time you've launched DBeaver, you'll probably be prompted with the Create new connection dialog.
Expand the SQL Server node, select jTDS driver, and click Next >.
For this tutorial I selected jTDS driver, but by all means select another driver if you prefer.
If the Create new connection wizard doesn't automatically appear when you open DBeaver, go to Database > New Connection to initiate this wizard.
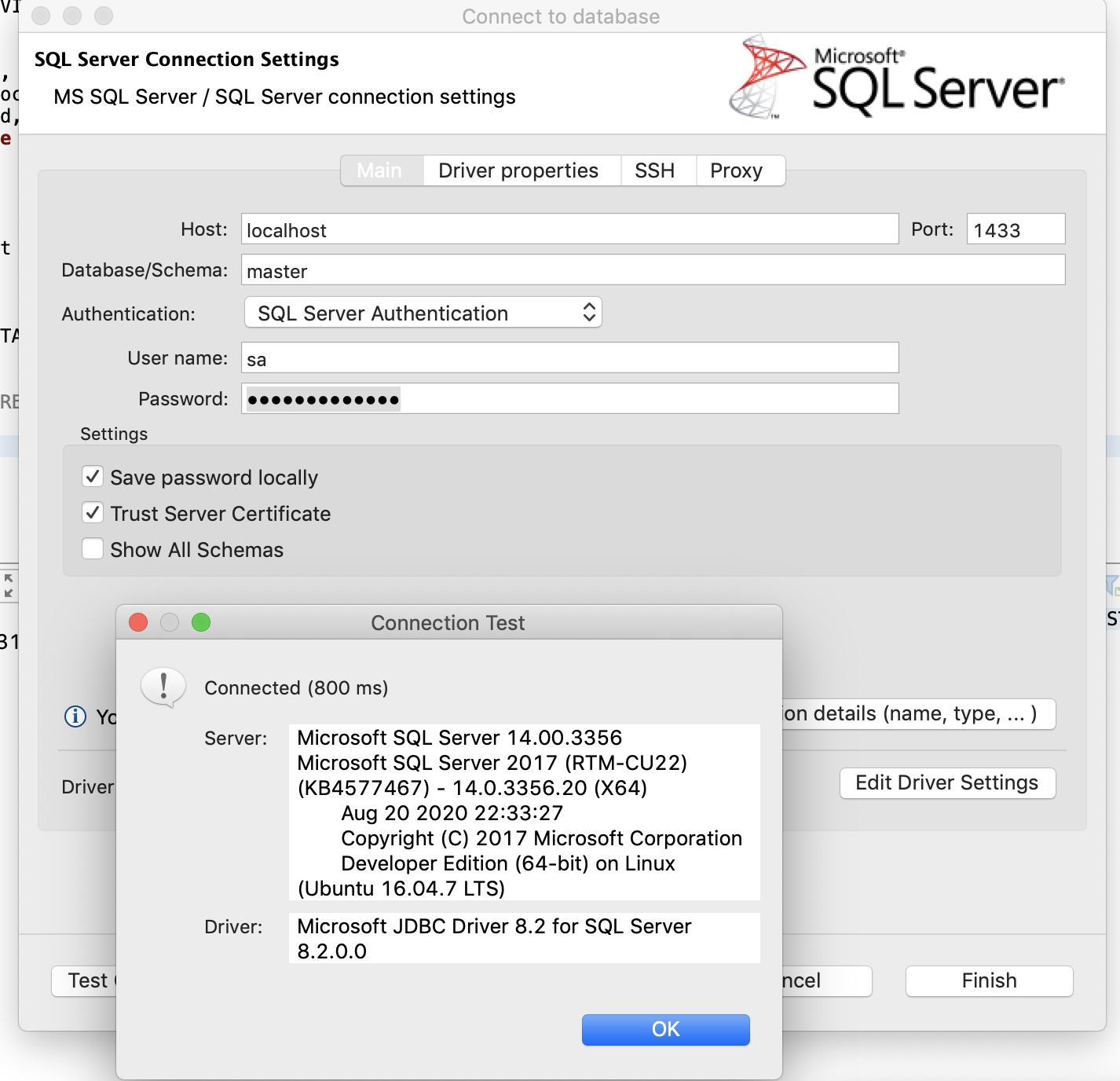
Enter Connection Settings
Enter the connection settings for the SQL Server instance that you'd like to connect to.
If the SQL Server instance is running on your local machine, use localhost.
Also click Test Connection to see if there are going to be any problems with the connection or not.
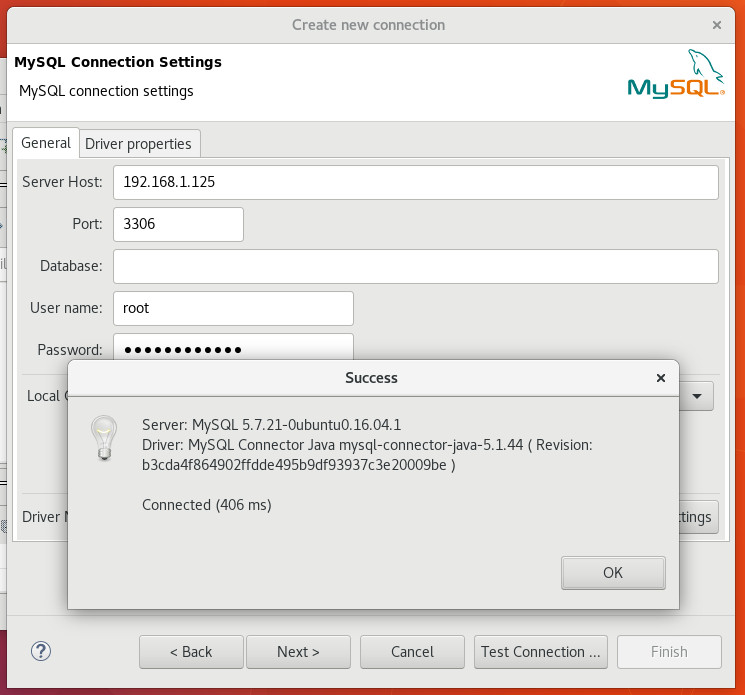
Download Driver Files (if required)
The connection wizard will tell you if you need to download any driver files. If you do, select the file/s and click Download.
Success Dialog Box
Once the driver has downloaded, a Success dialog is displayed. Click OK.
This dialog box would have appeared at the previous step if you didn't need to download a driver.
Continue with the Connection
Now that the driver has been downloaded, click Next > to continue with the connection.
Network Settings
This step gives you the option of entering any network settings that are required to access the SQL Server.
In this case, the SQL Server is running locally, so leave the default settings and click Next >.
Finish
Change any settings as required. For this tutorial, I left them all at the default settings.
Click Finish to create the connection.
Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Mac
That's it. We just made a new connection to SQL Server with DBeaver.
Dbeaver Local Client Mysql Ubuntu
The DBeaver interface is now displayed:

